Understanding ATPL Brain Disease: Symptoms & Causes
What is the impact of certain neurological conditions on aviation professionals? A specific form of cognitive impairment poses significant challenges for pilots and air traffic controllers.
Certain neurological conditions can impair cognitive function, impacting judgment, reaction time, and attention span crucial skills for pilots and air traffic controllers. These impairments can manifest in various ways, including difficulties with spatial reasoning, memory, and complex problem-solving. Examples range from mild attention deficits to more severe conditions affecting a professional's ability to perform their duties safely and effectively. The specific nature of these challenges depends on the underlying neurological condition and its severity.
The implications for aviation safety are substantial. Maintaining a high degree of mental acuity is paramount in aviation. Conditions affecting cognitive abilities could compromise decision-making in critical situations, potentially leading to accidents or incidents. Comprehensive and rigorous medical evaluations are essential for all aviation professionals, ensuring only those with the necessary cognitive abilities remain in these crucial roles. The importance of rigorous ongoing medical surveillance and the development of objective diagnostic tools cannot be overstated. Awareness of the potential impact of neurological conditions is a vital element for both professionals and regulatory bodies.
- Mi Corazn Es Tuyo Cast More Everything You Need To Know
- Nicky Gile Onlyfans Leaks What You Need To Know
The following sections will delve into specific neurocognitive conditions, their effects, and the measures implemented to ensure aviation safety in the context of neurocognitive impairment. This will include discussion of the medical evaluation processes, training protocols, and regulatory frameworks.
Neurological Conditions in Aviation Professionals
Neurological conditions impacting cognitive function present significant safety concerns for aviation professionals. Comprehensive understanding of these conditions is crucial for maintaining flight safety.
- Cognitive impairment
- Medical evaluations
- Safety regulations
- Pilot training
- Diagnostic tools
- Ongoing surveillance
- Aviation safety
Cognitive impairment, a key aspect, necessitates rigorous medical evaluations. Safety regulations dictate standards for pilots and controllers. Specialized pilot training programs address the cognitive demands of flight. Developing reliable diagnostic tools is crucial. Ongoing surveillance for neurological conditions is essential. Aviation safety relies heavily on adherence to these aspects. For example, a pilot with a diagnosed condition impacting visual-spatial processing may require stricter evaluation procedures and alternative roles to maintain safety. These considerations underscore the critical balance between upholding safety standards and allowing individuals to contribute to the industry.
- Josh Allen Sean Mcdermott Contracts Salaries Bills Future
- Cory Michael Smiths Dating Life Who Is He With In 2024
1. Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions affecting various mental functions, including memory, attention, language, and executive function. Within the context of aviation, certain forms of cognitive impairment can significantly impact safety. A crucial link exists between cognitive impairment and specific neurological conditions affecting aviators. These conditions, potentially encompassing a range of diagnoses, can subtly or profoundly affect an individual's ability to perform crucial tasks, like piloting or air traffic control, demanding sustained attention, quick decision-making, and complex problem-solving. The practical significance of recognizing this link lies in the need for rigorous medical evaluations to ensure pilots and controllers maintain the necessary cognitive abilities for safe operation.
The impact of cognitive impairment on aviation safety is substantial. For example, subtle deficits in attention or working memory could lead to missed signals or errors in judgment during critical phases of flight. Impaired spatial reasoning or decision-making could result in hazardous maneuvers. Conditions like mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), even without severe symptoms, can manifest as subtle cognitive impairments impacting crucial aviation skills. Moreover, underlying conditions like multiple sclerosis, or other neurological disorders, can progressively erode cognitive function, ultimately jeopardizing safety. Understanding the correlation between cognitive impairment and these conditions is vital for preventive measures and appropriate risk management.
In conclusion, cognitive impairment poses a considerable threat to aviation safety. A clear understanding of how specific neurological conditions can manifest as cognitive impairment is essential for comprehensive medical evaluations. Rigorous screening processes and ongoing monitoring of professionals are necessary. This knowledge is crucial for establishing safety standards and mitigating risks. Consequently, an informed and proactive approach to managing the effects of cognitive impairment in aviation settings is not just advisable; it is paramount for ensuring the safety of all involved.
2. Medical Evaluations
Medical evaluations play a critical role in assessing the fitness of aviation professionals, particularly concerning potential neurological conditions that could compromise safety. The rigorous process aims to identify any pre-existing or developing conditions that might impair cognitive functiona direct concern related to maintaining safe flight operations. These evaluations are essential to ensure individuals possessing the necessary mental acuity remain in roles requiring complex decision-making and rapid response.
- Comprehensive Examinations
Thorough physical and neurological examinations are fundamental. These assessments evaluate a wide range of cognitive functions, including memory, attention span, reaction time, and visual-spatial processing. Specific tests may assess vestibular function, balance, and coordination. Examples include neuropsychological testing, electroencephalography (EEG), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in cases where further investigation is warranted. These assessments provide detailed information about the individual's neurological status, aiding in identifying potential risks and influencing safety decisions.
- History Taking and Reporting
Detailed medical histories are crucial. This includes a thorough inquiry into any prior or present neurological conditions, injuries, or treatments. A comprehensive report from the individual's primary physician, including a detailed medical history and current medications, provides further context. This ensures a complete picture of the individual's health status and potential risk factors related to safety in aviation. Examples include noting previous concussions, symptoms of dizziness or balance problems, or any reported cognitive difficulties.
- Assessment of Aviation-Specific Skills
Medical evaluations in aviation extend beyond general neurological assessments. They often incorporate tests that evaluate the individual's specific aviation skills, such as simulator-based tasks and simulated emergency situations. These evaluations assess how neurological conditions may affect the individual's capacity to handle the high-stakes environment of flight or air traffic control. This practical testing method provides a more specific indication of the individual's fitness for duty. Examples include tests mimicking flight maneuvers, emergency procedures, and decision-making under pressure.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up evaluations are crucial. This allows for identifying any changes in neurological status that might develop over time. This ongoing assessment is important for those with pre-existing conditions, ensuring continued suitability for their chosen role. Regular monitoring, facilitated by communication with the individual's physician, facilitates detection of subtle or progressive conditions. This approach emphasizes a proactive safety strategy.
In summary, medical evaluations provide a comprehensive and layered approach to determining suitability for aviation-related professions. They mitigate risks associated with neurological conditions potentially impacting cognitive function, thus maintaining high standards of aviation safety. Regular and rigorous medical evaluations are paramount in ensuring the safety and well-being of all involved in aviation operations.
3. Safety Regulations
Safety regulations in aviation are crucial for mitigating risks associated with neurological conditions that could compromise flight safety. These regulations establish standards for medical evaluations, training, and ongoing monitoring, ensuring individuals operating aircraft and air traffic control systems possess the necessary cognitive abilities to handle complex situations. The direct link between safety regulations and potential neurological conditions is paramount, especially considering the potential consequences of impaired judgment or reaction time.
- Medical Certification Standards
Regulations dictate specific medical standards for aviation professionals. These standards outline the required examinations and evaluations, including those for conditions potentially impacting cognitive function. Examples include standards demanding specific cognitive scores for certification, mandated neuropsychological assessments, and the required reporting of any condition that may affect an aviator's performance. These standards ensure individuals meet minimum criteria for safe operation, minimizing the risk associated with certain neurological conditions.
- Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
Regulations mandate the reporting of any medical condition that could potentially impair an aviator's cognitive function. This includes conditions diagnosed after certification. Examples include reporting incidents like concussions or suspected neurological disorders. These requirements ensure that safety authorities are aware of any factors affecting an aviator's ability to perform tasks adequately. This proactivity safeguards against unforeseen issues.
- Re-certification Processes
Regulations require periodic re-certification to maintain pilot or air traffic controller licenses. This ongoing monitoring process ensures that any deterioration in cognitive function due to a developing condition or a previously undiagnosed condition is detected, and appropriate actions taken. Examples include mandatory checkups at specified intervals and reassessments based on the results of those checkups. Proactive re-evaluation and possible license restrictions help maintain safety.
- Operational Limitations and Restrictions
Regulations may impose limitations or restrictions on the activities of individuals with diagnosed conditions impacting cognitive abilities. These restrictions are often case-specific. Examples include limiting the types of flight operations or assigning roles that better suit an individual's cognitive abilities. By enabling tailored adjustments, these regulations ensure that individuals with conditions do not engage in activities beyond their safe capacity. These measures balance the individual's rights and needs with the demands of aviation safety.
In summary, safety regulations play a crucial role in managing the complexities surrounding potential neurological conditions and cognitive impairment in aviation. These regulations establish standards, mandate reporting, and implement ongoing monitoring, all designed to protect aviation safety. The rigor of these regulations reflects a deep commitment to maintaining the highest standards for safe flight operations.
4. Pilot Training
Pilot training programs are designed to equip individuals with the cognitive skills and practical abilities necessary for safe flight operations. These programs address the demands of aviation, encompassing mental acuity, decision-making, and rapid response to critical situations. The connection between pilot training and potential neurological conditions impacting cognitive function is vital. Effective training programs must consider and adapt to the unique needs of individuals, acknowledging that cognitive impairments, even subtle ones, could affect performance during flight. Appropriate adjustments to training protocols and materials are crucial, not just to address pre-existing conditions, but also potential ones that might emerge over time.
Specific training elements, like simulator exercises, are essential in evaluating an individual's performance under pressure, highlighting potential vulnerabilities related to cognitive function. Realistic scenarios and complex problem-solving exercises in training environments can reveal potential weaknesses in an individual's cognitive processing. Furthermore, incorporating medical evaluations into training protocols allows for proactive identification of potential risks. This proactive approach ensures that individuals with subtle or pre-existing conditions are identified and managed appropriately, reducing the likelihood of safety compromise during actual flight operations. This strategy also assists in the development of tailored training programs that acknowledge and accommodate individual needs.
In conclusion, pilot training plays a significant role in mitigating the potential impact of neurological conditions, often referred to as cognitive impairment, on safety. By incorporating a proactive and comprehensive approach to training programs, addressing potential risks, and adapting training methods as necessary, the aviation industry enhances the safety of flight operations. Training's role extends beyond the acquisition of technical skills to encompass the development and reinforcement of cognitive capabilities crucial for safe and effective performance in challenging situations. This holistic approach prioritizes both the individual's well-being and the safety of all involved in the aviation industry.
5. Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis of neurological conditions impacting aviation professionals is paramount. Effective diagnostic tools are essential for identifying and assessing the potential impact of such conditions on cognitive function and safety. The reliability and sensitivity of these tools directly influence the ability to identify and manage individuals at risk, ultimately safeguarding aviation safety.
- Neuropsychological Testing
Neuropsychological testing provides a comprehensive evaluation of cognitive abilities, including memory, attention, processing speed, and executive functions. These assessments are crucial for detecting subtle impairments that might not be apparent in routine physical examinations. Examples include tests measuring reaction time, working memory capacity, and problem-solving skills. This information assists in determining the presence and extent of cognitive impairment, which is vital for assessing fitness for duty in aviation. A key implication is the ability to identify subtle deficits in cognitive function, enabling early intervention and appropriate adjustments in operational responsibilities.
- Neuroimaging Techniques
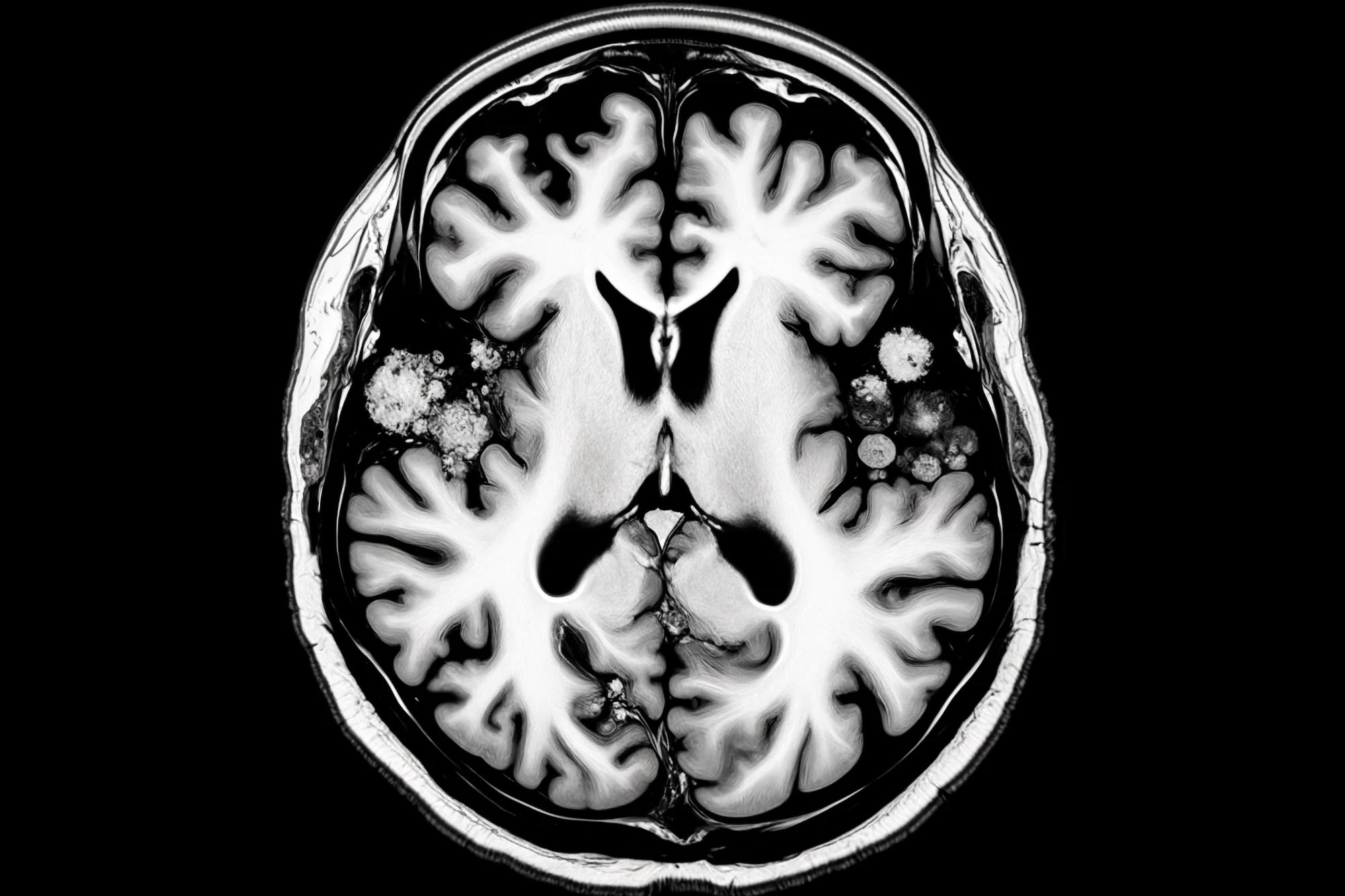
Neuroimaging techniques, like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT), offer detailed visualizations of the brain structure. These methods can reveal abnormalities or lesions suggestive of neurological conditions, which may contribute to cognitive impairment. MRI, for instance, is often used to identify structural damage, while CT scanning can reveal bleeding or other acute pathologies. Examples include detecting tumors, strokes, or traumatic brain injuries, all of which can significantly affect cognitive function. The implication lies in identifying the cause of any cognitive dysfunction, aiding in a precise diagnosis and informed decisions regarding ongoing safety management.
- Electrophysiological Measures
Electrophysiological measures, such as electroencephalography (EEG), measure electrical activity within the brain. Anomalies in brainwave patterns can indicate various neurological disorders affecting cognitive processes. EEG can detect abnormalities in brain activity that might correlate with impairments in alertness, attention, or memory. These measures are instrumental in assessing neurological function, offering insights into potential cognitive impairments. Examples include identifying sleep disorders or abnormal electrical activity that may impair alertness. This allows for a more complete understanding of the individual's neurological state, facilitating a more informed and specific diagnostic approach.
- Vestibular Testing
Vestibular testing assesses the function of the inner ear, which is crucial for balance and spatial orientation. Impaired vestibular function can lead to dizziness, vertigo, and balance issues, affecting spatial awareness. Examples include tests assessing eye movements during head rotation or posture evaluation. The implications relate directly to the safety of flight, as difficulties with balance and spatial awareness can lead to loss of coordination in flight or during air traffic control. Early detection of such problems allows for appropriate adjustments or restrictions in duties.
Effective diagnostic tools are pivotal in evaluating the relationship between neurological conditions and aviation safety. By combining these techniques, clinicians can form a comprehensive picture of an individual's cognitive abilities, leading to a more accurate and comprehensive diagnosis. The information gained from these tools is critical in determining the appropriateness of continued aviation duties and mitigating the risks of cognitive impairment. Comprehensive assessments are crucial for responsible evaluations and safety protocols.
6. Ongoing Surveillance
Ongoing surveillance, a critical component of aviation safety, is essential for mitigating the risks associated with neurological conditions affecting cognitive function. This proactive approach involves continuous monitoring of aviators' health, specifically regarding potential or emerging neurological issues, often referred to as "atpl brain disease." The primary goal is early detection of any condition that could impact the aviator's ability to perform crucial tasks, such as piloting or air traffic control, which demands sustained attention, rapid decision-making, and complex problem-solving. Failure to maintain vigilance in this area can have severe consequences, highlighting the urgent need for consistent surveillance measures.
The practical significance of ongoing surveillance is underscored by the fact that some neurological conditions develop subtly over time. Early detection and intervention are vital to minimizing potential risks to flight safety. For example, a pilot experiencing subtle cognitive changes might initially go unnoticed, but with ongoing surveillance, the progression of a condition like mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) can be observed, allowing for adjustments in operational roles or medical interventions. This approach prevents a gradual decline that could compromise safety, while enabling adjustments to work assignments that minimize the impact of the condition. Further, this approach addresses concerns related to potential progressive deterioration of cognitive function, enabling suitable accommodations, such as reduced workload or specific procedural adjustments. Regular monitoring enables appropriate adaptations, potentially preventing incidents or accidents. The aim is to keep the individual and the airspace as safe as possible.
In conclusion, ongoing surveillance is not merely a procedural requirement but a critical element in maintaining aviation safety. It allows for the early identification of potential issues related to neurological health and cognitive function, enabling proactive mitigation strategies and ultimately reducing risks associated with such conditions. This approach not only safeguards the individuals involved but also protects the safety of all those impacted by the aviation system. Regular monitoring and assessment are essential to ensuring ongoing fitness for duty, aligning with regulatory requirements and prioritizing the highest safety standards.
7. Aviation Safety
Aviation safety is paramount, demanding unwavering vigilance in maintaining optimal cognitive function amongst personnel responsible for flight operations. Conditions affecting brain health, often referred to as "atpl brain disease," pose a direct threat to safety protocols. This exploration examines crucial aspects of aviation safety in relation to such neurological concerns, emphasizing the need for meticulous evaluation and proactive management.
- Medical Certification Standards
Rigorous medical certification processes are fundamental. These standards necessitate comprehensive evaluations of individuals' cognitive abilities, aiming to identify any neurological condition that might compromise safety. Failure to adhere to these standards can lead to compromised decision-making, reaction time, and vigilance during critical flight phases. This includes thorough examinations, neuropsychological testing, and the assessment of factors like pre-existing conditions and potential risks. Exemplars of such conditions that can be detected include those affecting memory, attention, spatial awareness, and judgment.
- Pilot Training Protocols
Pilot training protocols must include assessments of cognitive function and reaction time. Simulations and exercises mimicking high-pressure scenarios are crucial to detect any limitations stemming from neurological conditions. Recognizing potential effects of neurological issues on critical tasks like situational awareness, decision-making, and emergency response are fundamental aspects of robust training programs. This approach highlights the importance of individualized assessments of cognitive capabilities.
- Continuous Monitoring and Surveillance
Ongoing surveillance of pilots and other aviation professionals is vital. Regular medical checkups, coupled with rigorous reporting systems, enable early detection of developing conditions or exacerbations of pre-existing neurological issues. This proactive approach minimizes risks associated with gradual decline or onset of neurological disorders. Effective ongoing surveillance systems incorporate methods like regular medical examinations and self-reporting protocols to identify and manage possible neurological concerns.
- Operational Limitations and Adjustments
Safety regulations often necessitate adjustments to operational roles based on individual assessments. This may involve assigning roles compatible with an individual's cognitive capabilities or imposing operational limitations. For instance, pilots diagnosed with conditions affecting specific cognitive functions, such as spatial reasoning, might be assigned roles where these functions are less critical. This ensures the continued safety of flight operations while adapting to the individual's capabilities. Careful consideration of these adjustments can proactively minimize safety risks.
These facets demonstrate a multifaceted approach to integrating aviation safety standards with the challenges presented by "atpl brain disease." The interconnectedness of rigorous medical assessments, tailored training, continuous monitoring, and responsive operational adjustments form the cornerstone of a robust safety framework. By prioritizing these interconnected aspects, the aviation industry actively mitigates risks and upholds the highest safety standards.
Frequently Asked Questions about Neurological Conditions in Aviation
This section addresses common inquiries regarding neurological conditions that might affect aviation professionals. Accurate information and understanding are essential for maintaining safety standards within the aviation industry.
Question 1: What are the types of neurological conditions potentially affecting aviation professionals?
Neurological conditions impacting aviators encompass a spectrum of disorders, including, but not limited to, mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), multiple sclerosis, seizures, and other conditions affecting cognitive function, balance, or coordination. Specific details and diagnoses depend on individual cases.
Question 2: How are neurological conditions evaluated in aviation professionals?
Medical evaluations are highly specialized and comprehensive. These include thorough medical histories, physical examinations, neuropsychological testing, and often neuroimaging techniques like MRI or EEG. Aviation medical examiners employ standardized procedures and criteria to determine fitness for duty.
Question 3: What role do safety regulations play in managing these conditions?
Safety regulations establish clear medical standards and reporting requirements for aviation professionals. These regulations mandate the reporting of any diagnosed or suspected neurological condition, enabling the identification of potential risks and the implementation of appropriate operational adjustments.
Question 4: How does pilot training address the potential impact of neurological conditions?
Pilot training programs must incorporate assessments of cognitive function and reaction time. Simulations and exercises in high-pressure scenarios allow for the identification of potential weaknesses related to neurological function. Tailored training adaptations are vital for addressing identified vulnerabilities.
Question 5: What measures are in place for ongoing monitoring of these conditions?
Continuous monitoring of aviation professionals is critical. This includes periodic medical evaluations, and the reporting of any changes or new symptoms. Rigorous surveillance and prompt responses to any concerning developments are crucial aspects of maintaining safety.
Understanding the complexities of neurological conditions impacting aviation professionals necessitates a multifaceted approach. The aviation industry relies on stringent medical standards, rigorous training, and ongoing surveillance to uphold the highest safety protocols. This rigorous approach is paramount to ensuring the well-being of all involved.
The next section will delve into specific strategies for minimizing the impact of neurological conditions on aviation safety.
Conclusion
This exploration of neurological conditions impacting aviation professionals underscores the critical link between brain health and flight safety. Key findings highlight the multifaceted nature of the challenge, emphasizing the necessity for rigorous medical evaluations, comprehensive training protocols, and ongoing surveillance. The importance of accurate diagnosis through neuropsychological testing, neuroimaging, and electrophysiological measures cannot be overstated. The article demonstrates that effective management of conditions affecting cognitive function, balance, or coordination demands a tailored approach, incorporating adjustments to operational roles and responsibilities. Safety regulations and reporting mechanisms are essential to proactive identification and mitigation of risks. Moreover, pilot training programs must effectively address the potential impact of these conditions on crucial aspects of flight operations, including decision-making, reaction time, and situational awareness. Ultimately, the article emphasizes that safeguarding aviation safety requires a comprehensive, integrated approach that acknowledges the complexity of individual neurological variations and their potential impact on performance.
The imperative for prioritizing brain health in aviation is undeniable. The consequences of overlooking or inadequately managing neurological conditions are severe and potentially catastrophic. Ongoing research, development of advanced diagnostic tools, and the refinement of safety protocols are essential to minimize risks. Aviation professionals, regulatory bodies, and healthcare providers must collaborate to establish and maintain the highest standards of safety, recognizing the enduring importance of protecting both individual well-being and the safety of those relying on aviation systems. Failure to do so jeopardizes the very foundation of safe flight operations.
Article Recommendations

Detail Author:
- Name : Joy Beahan
- Username : bwillms
- Email : baumbach.mateo@wuckert.com
- Birthdate : 1988-05-15
- Address : 231 Schmeler River Suite 354 Bayerchester, MO 14999-7389
- Phone : 325-413-2941
- Company : Gibson, Schroeder and Smith
- Job : Stationary Engineer OR Boiler Operator
- Bio : Adipisci placeat deserunt ipsum. Ut et consequatur similique eos deleniti alias. Doloribus incidunt ad sit asperiores. Eos sit similique eligendi soluta optio sequi.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/nienow2020
- username : nienow2020
- bio : Sint quisquam nisi culpa facere.
- followers : 528
- following : 750
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@vnienow
- username : vnienow
- bio : Ut quaerat eum animi sapiente reiciendis iure ut eos.
- followers : 2649
- following : 1094
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/vern.nienow
- username : vern.nienow
- bio : Modi repellendus cupiditate exercitationem atque.
- followers : 4632
- following : 1780